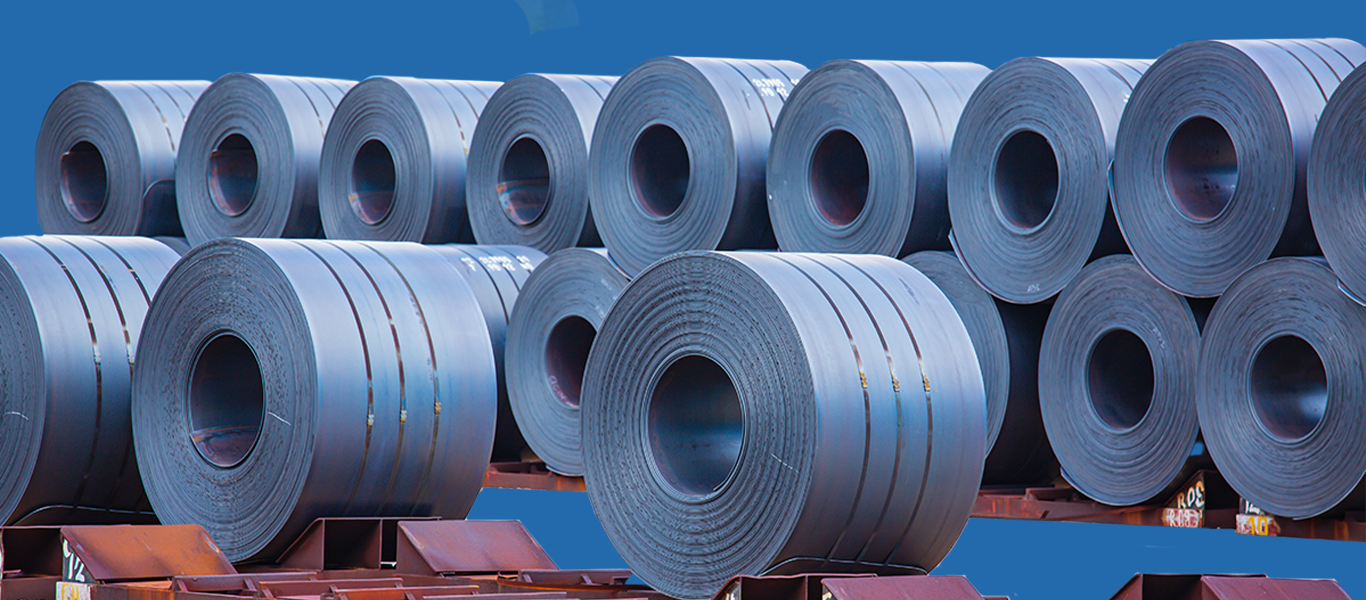
In many industries, hot-rolled steel is an important material and used in many ways. It’s made through a special process that makes it strong and good for lots of jobs. Let’s explore what makes hot-rolled steel special, how it’s made, and all the different things it’s used for.
Understanding the Process of Making Hot-Rolled Steel:
Hot-rolled steel is created through a systematic process designed to enhance its structural integrity and flexibility. The journey begins with heating large steel slabs above their recrystallization temperature, typically around 1700°F (926°C), in a controlled environment. This high temperature ensures the steel becomes malleable, allowing for reshaping without compromising its strength.
Once heated to the optimal temperature, the steel slabs are passed through a series of rollers, exerting tremendous pressure to shape them into desired forms. This process, known as hot rolling, results in the formation of long sheets or coils of hot-rolled steel, characterized by its scaled surface finish.
Key Properties of Hot-Rolled Steel:
Hot-rolled steel is known for several distinctive properties that make it a preferred choice for numerous industrial and construction applications:
Strength and Durability:
Hot-rolled steel showcases exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for load-bearing structures and heavy machinery components.
Malleability:
The hot-rolling process imparts malleability to the steel, enabling easy molding into various shapes and forms without compromising its structural integrity.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to its cold-rolled counterpart, hot-rolled steel is generally more cost-effective, making it an excellent option for large-scale construction projects and industrial manufacturing.
Versatility:
Hot-rolled steel comes in a wide range of thicknesses and dimensions, catering to diverse application requirements across industries.
Exploring the Uses of Hot-Rolled Steel:
Construction Industry:
The construction sector is one of the largest consumers of hot-rolled steel, utilizing it for an extensive range of structural components, including:
Beams and Columns:
Hot-rolled steel beams and columns provide vital support for buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects, owing to their exceptional load-bearing capacity and structural integrity.
Railroad Tracks and Infrastructure:
Hot-rolled steel is essential to the construction of railroad tracks, bridges, and other transportation infrastructure, ensuring longevity under heavy loads and adverse environmental conditions.
Manufacturing Sector:
In the manufacturing industry, hot-rolled steel finds application in the fabrication of:
Automotive Components:
Hot-rolled steel sheets are used in the manufacturing of automobile frames, chassis, and structural components due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and formability.
Industrial Machinery:
Machinery and equipment manufacturers utilize hot-rolled steel for constructing heavy-duty machinery components, such as gears, shafts, and frames, requiring superior strength and durability.
Energy and Infrastructure Projects:
Hot-rolled steel plays a pivotal role in energy production and infrastructure development, including:
Oil and Gas Pipelines:
The oil and gas industry rely on hot-rolled steel for constructing pipelines, storage tanks, and drilling equipment, ensuring reliability and resilience in harsh operating environments.
Power Generation Facilities:
Hot-rolled steel is utilized in the construction of power plants, including thermal, nuclear, and renewable energy facilities, supporting critical infrastructure components such as turbines, boilers, and transmission towers.
The Role of Hot-Rolled Steel Suppliers and Manufacturers:
Hot-rolled steel suppliers and manufacturers serve as vital contributors to various industries, ensuring a consistent supply of quality material tailored to meet specific application requirements. These entities leverage advanced manufacturing processes and stringent quality control measures to deliver hot-rolled steel products that adhere to industry standards and specifications.
Conclusion:
In essence, hot-rolled steel stands as a cornerstone material in modern industrial and construction applications. Owing to its exceptional properties, versatility, and widespread availability, this material is fundamental for the success of many industries. From towering skyscrapers to intricate machinery, hot-rolled steel serves as the backbone of countless structures and systems, highlighting its vital role in driving progress and innovation across diverse sectors. As industries continue to evolve and expand, the demand for hot-rolled steel is poised to keep growing, reaffirming its status as a quintessential material in the global manufacturing landscape.